Hawaii Route 98 is a 1.8-mile State Highway located on the Island of O'ahu in the City of Honolulu. The entirety of Hawaii Route 98 is aligned on Vineyard Boulevard from Interstate H-1/Luanlilo Freeway Exit 20B to Exit 22.
Part 1; the history of Hawaii Route 98
Prior to the Statehood the first signed highways within Hawaii Territory came into existence during World War II. During World War II the territory of Hawaii saw an influx of military activity following the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7th, 1941. Numerous Military Routes and early Hawaii Routes were signed through the Hawaiian Territory to aid military personnel in navigating the islands. Military Highways were assigned US Route style shields whereas lesser highways were assigned an early variation of what is now the Hawaii Route Spade. What is now Vineyard Boulevard in Boulevard was originally known as Vineland Street and did not have a World War II era Hawaii Route assigned to it. Vineyard Street was named after the numerous vineyards which used to line it. A full version of the 1946 Army Map of O'ahu can be seen on hawaiihighways.com here.
The beginnings of what is now known as the Lunalilo Freeway was completed in downtown Honolulu as the Mauka Arterial during November 1953. The Mauka Arterial was approximately 1 mile length between Kapiolani Boulevard westward to Kapiolani Hospital at Punahou Street.
Circa 1955 following the conclusion of World War II the United States Bureau of Public Roads renumbered the Hawaii Route System. The 1955 Hawaii Route Renumbering saw most of the conventions utilized by the current Hawaii State Route System established. Primary Hawaii Routes were given two digit numbers whereas Secondary Hawaii Routes were given three digit numbers. The Hawaii Routes were assigned in sequence for what Island/County they were located on coupled with what Federal Aid Program number they were tied to. In the case of O'ahu the Island was assigned numbers in the range of 60-99. In the case of the Mauka Arterial corridor it was initially assigned as part of Hawaii Route 72. A far more detailed explanation of the 1955 Hawaii Route Renumbering can be found at hawaiihighways.com here.
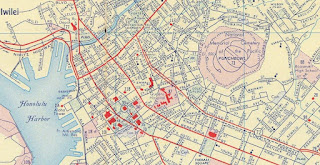
The planned corridor of the Mauka Arterial can be observed on the 1956 Shell Highway Map of Honolulu. The Mauka Arterial is shown having a planned connection to Vineyard Street.
The 1959 Gousha Map of Hawaii shows the Vineland Street extension acting as part of the interim alignment of Hawaii Route 72 while the Lunalilo Freeway was under construction. Hawaii Route 72 is shown diverting from the end of the completed Lunalilo Freeway segment onto Lunalilo Boulevard west to the Vineyard Street extension. Hawaii Route 72 is shown aligned on Vineyard Street west to Nuuanu Boulevard and southward to Beretania Street. Notably the Vineyard Street extension is not shown to be yet continuous with the existing segment west of Foster Botanical Garden.
Interstate H-1 on the Queen Liliuokalani Freeway from Exit 5 (Hawaii Route 76/Hawaii Route 750) to its western terminus opened during 1967. The remainder of the Lunalilo Freeway segment of Interstate H-1 in Honolulu was completed by July 1969. The entirety of Vineyard Boulevard can be seen assigned as Hawaii Route 98 on the October 1968 Interstate H-4 proposal document titled: Proposed Route H-4.





























Comments