Kalākaua Avenue ("Kalakaua Avenue") is a major city street in the City of Honolulu on the Hawaiian island of O'ahu. Kalakaua Avenue originates in the neighborhood of Makiki near Interstate H-1. Kalakaua Avenue follows a generally eastward course through McCully-Moiliili over the Ala Wai Canel into Waikiki. Kalakaua Avenue through Waikiki is generally a one-way through road which terminates near Diamond Head Crater.
This page is part of the Gribblenation Hawaii Roads series. A compellation of all Hawaii-related media from both Gribblenation and RoadwayWiz can be found by clicking here.
Part 1; a brief history of Kalākaua Avenue
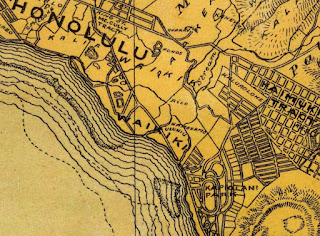
What is now Kalakaua Avenue has been the main point of entry into Waikiki since the 19th Century when it was known as Waikiki Road. Stage service opened for service on Waikiki Road during 1868 which was replaced by a horse driven tramcar system in 1888. Below Waikiki Road can be seen on the 1881 C.J. Lyons Map of O'ahu.Waikiki Road can be seen as the main highway through Waikiki on the 1899 J.T. Taylor Map of O'ahu.
During 1901 electric trolley service opened on Waikii Road. Waikiki Road was renamed during 1908 to Kalakaua Avenue in honor of the last King of Hawaii Kalākaua. Kalakaua Avenue modernized significantly upon the completion of the Ala Wai Canal in 1928. The Ala Wai Canal shunted stream run off into Waikiki which allowed it to transform from a wet land into the tourism district of Honolulu.
During World War II the territory of Hawaii saw an influx of military activity following the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7th, 1941. Numerous Military Routes and early Hawaii Routes were signed through the Hawaiian Territory to aid military personnel in navigating the islands. Military Highways were assigned US Route style shields whereas lesser highways were assigned an early variation of what is now the Hawaii Route Spade. A 1946 Army Map of the Island of O'ahu Kalakaua Avenue in Waikiki was assigned as part of Hawaii Route 101. Kalakaua Avenue was an important military connector due to the presence of Fort DeRussy in Waikiki and Fort Ruger at Diamond Head Crater.
From Interstate H-1 traffic is directed to use Exit 23 onto Punahoa Street to reach Waikiki.
From Punahoa Street southbound traffic can access Kalakaua Avenue by turning west onto Beretania Street. From westbound Beretania Street traffic can access Kalakaua Avenue southbound.
Kalakaua Avenue southbound passes through Makiki and McCully-Moiliili to the Ala Wai Canal into Waikiki.
The Fort DeRussy Military Reservation in Waikiki is under the jurisdiction of the U.S. Army but functions more as a park during modern times. Fort DeRussy was originally constructed during 1911 along with Battery Randolph. Battery Randolph now houses the U.S. Army Museum of Hawaii.
From Fort DeRussy Beach one can see how much Diamond Head Crater towers of Waikiki.
Kalakaua Avenue has several all-way pedestrian crossings such as the one below at Lewers Street.
Featured below is a Blue Stop Sign seen at Lauula Street and Lewers Street just east of Kalakaua Avenue. Blue Stop Signs are typically seen in Hawaii on private drives given the State prohibits official looking signage.
During June of 2019 Dan Murphy of the Roadwaywiz Youtube Channel (and Gribblenation) featured real-time drives on Kalakaua Avenue. Below Kalakaua Avenue can be viewed headed eastbound during the daytime.
Below Kalakaua Avenue can be viewed headed eastbound during the nighttime.


































Comments