In December of 2017 I drove the entirety of California State Route 165.
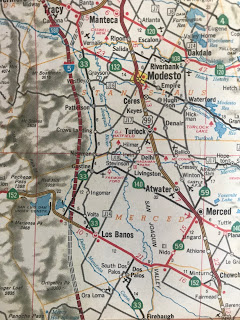
CA 165 is a 38 mile north/south state highway traveling from CA 99 in Turlock to I-5 south of Los Banos.
Part 1; a drive on California State Route 165
My approach to CA 165 southbound was from CA 99 in Turlock.
From the Lander Avenue Exit traffic can turn left for Signed County Route J14 north and right for CA 165 south.
South of Turlock CA 165 runs on Lander Avenue. All of CA 165 is designated as a Safety Corridor and has heavy truck traffic between CA 99 in Turlock south to CA 152/33 in Los Banos.
Just north of Hilmar CA 165 exits Stanislaus County and enters Merced county.
Hilmar is 4 miles south of Turlock on CA 165. Hilmar dates back to the late 1910s and once the southern terminus of the now defunct Tidewater Southern Railway. The community is mostly known today as the location of the Hilmar Cheese Company which just so happens to be located on CA 165.
South of Hilmar CA 165 twists around farm parcels on an approach to a bridge over the Merced River.
South of the Merced River CA 165 briefly multiplexes the east/west County Route J18 from River Road to Westside Boulevard.
CA 165 south next enters Stevinson which apparently dates back to the 1900s.
CA 165 junctions CA 140 in Stevinson.
South of CA 140 the routing of CA 165 crosses the San Joaquin River and enters Great Grass Lands State Park and San Luis National Wildlife Refuge. Both parks are undeveloped marsh land along the San Joaquin River and a fairly decent analog as to how wet San Joaquin Valley used to be. Despite the low rain levels this winter there was still plenty of water pouring into the surrounding landscape from the San Joaquin River.
CA 165 enters Los Banos and junctions CA 152/33 at Pacheco Boulevard. CA 165 south of CA 152/33 is signed as "To I-5."
CA 165 south of Los Banos is signed on Mercey Springs Road which I find to be odd since there doesn't appear to be a through route connecting to the actual springs. I did find this nice little wood/concrete bridge south of Los Banos on CA 165 on the Main Canal. The bridge date is listed as being completed in 1949 which was well before the state was involved in maintenance.
Approaching the Diablo Range CA 165 crosses the California Aqueduct San Luis Canal.
CA 165 ends at I-5 and has a proper shield/end placard combination.
Part 2; the history of the California State Route 165 designation
The current CA 165 is the second highway to carry the designation. The original CA 165 was a temporary connecting route between I-5 and CA 60 via Indian Street in Los Angeles County. According to CAhighways the original CA 165 defined in 1963 and was part of Legislative Route 230 which was added to the State Highway System in 1947. The first CA 165 can be seen on the 1964 Division of Highways State Map.
The original CA 165 was deleted in 1965 according to CAhighways. CA 165 was recycled into the current highway in 1970. By 1975 CA 165 is shown complete on the Caltrans State Highway Map from CA 140 south to I-5.
CA 165 appears on the 1979 Caltrans State Highway Map as a completed route from CA 140 north to CA 99.
The current CA 165 between CA 99 in Turlock and CA 33/152 in Los Banos was originally part of Signed County Route J14. J14 appears on the 1966 Goshua Highway Map signed between Turlock and Los Banos.
CA 165 is a 38 mile north/south state highway traveling from CA 99 in Turlock to I-5 south of Los Banos.
Part 1; a drive on California State Route 165
My approach to CA 165 southbound was from CA 99 in Turlock.
From the Lander Avenue Exit traffic can turn left for Signed County Route J14 north and right for CA 165 south.
South of Turlock CA 165 runs on Lander Avenue. All of CA 165 is designated as a Safety Corridor and has heavy truck traffic between CA 99 in Turlock south to CA 152/33 in Los Banos.
Just north of Hilmar CA 165 exits Stanislaus County and enters Merced county.
Hilmar is 4 miles south of Turlock on CA 165. Hilmar dates back to the late 1910s and once the southern terminus of the now defunct Tidewater Southern Railway. The community is mostly known today as the location of the Hilmar Cheese Company which just so happens to be located on CA 165.
South of Hilmar CA 165 twists around farm parcels on an approach to a bridge over the Merced River.
South of the Merced River CA 165 briefly multiplexes the east/west County Route J18 from River Road to Westside Boulevard.
CA 165 south next enters Stevinson which apparently dates back to the 1900s.
CA 165 junctions CA 140 in Stevinson.
South of CA 140 the routing of CA 165 crosses the San Joaquin River and enters Great Grass Lands State Park and San Luis National Wildlife Refuge. Both parks are undeveloped marsh land along the San Joaquin River and a fairly decent analog as to how wet San Joaquin Valley used to be. Despite the low rain levels this winter there was still plenty of water pouring into the surrounding landscape from the San Joaquin River.
CA 165 enters Los Banos and junctions CA 152/33 at Pacheco Boulevard. CA 165 south of CA 152/33 is signed as "To I-5."
CA 165 south of Los Banos is signed on Mercey Springs Road which I find to be odd since there doesn't appear to be a through route connecting to the actual springs. I did find this nice little wood/concrete bridge south of Los Banos on CA 165 on the Main Canal. The bridge date is listed as being completed in 1949 which was well before the state was involved in maintenance.
Approaching the Diablo Range CA 165 crosses the California Aqueduct San Luis Canal.
CA 165 ends at I-5 and has a proper shield/end placard combination.
Part 2; the history of the California State Route 165 designation
The current CA 165 is the second highway to carry the designation. The original CA 165 was a temporary connecting route between I-5 and CA 60 via Indian Street in Los Angeles County. According to CAhighways the original CA 165 defined in 1963 and was part of Legislative Route 230 which was added to the State Highway System in 1947. The first CA 165 can be seen on the 1964 Division of Highways State Map.
The original CA 165 was deleted in 1965 according to CAhighways. CA 165 was recycled into the current highway in 1970. By 1975 CA 165 is shown complete on the Caltrans State Highway Map from CA 140 south to I-5.
CA 165 appears on the 1979 Caltrans State Highway Map as a completed route from CA 140 north to CA 99.
The current CA 165 between CA 99 in Turlock and CA 33/152 in Los Banos was originally part of Signed County Route J14. J14 appears on the 1966 Goshua Highway Map signed between Turlock and Los Banos.































Comments