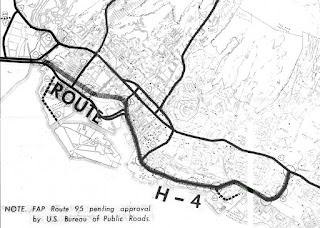
The Hawaiian Island of O'ahu is home to four Interstate Highways; H-1, H-2, H-3 and H-201. Had history gone slightly differently during the 1960s a fifth Interstate corridor on O'ahu could have been constructed through downtown Honolulu and the neighborhood of Waikiki. The proposed corridor of Interstate H-4 can be seen above as it was presented by the Hawaii Department of Transportation during October 1968.
This page is part of the Gribblenation O'ahu Highways page. All Gribblenation and Roadwaywiz media related to the highway system of O'ahu can be found at the link below:
https://www.gribblenation.org/p/gribblenation-oahu-highways-page.html
The history of proposed Interstate H-4
The corridor of Interstate H-4 was conceived as largely following what is now Hawaii Route 92 on Nimitz Highway and Ala Moana Boulevard. Prior to the Statehood the first signed highways within Hawaii Territory came into existence during World War II. During World War II the territory of Hawaii saw an influx of military activity following the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7th, 1941. Numerous Military Routes and early Hawaii Routes were signed through the Hawaiian Territory to aid military personnel in navigating the islands. Military Highways were assigned US Route style shields whereas lesser highways were assigned an early variation of what is now the Hawaii Route Spade.
A 1946 Army Map of the Island of O'ahu shows modern Nimitz Highway as part of Military Route 1 in Honolulu. A full version of the 1946 Army Map of O'ahu can be seen on hawaiihighways.com here.
Circa 1955 following the conclusion of World War II the United States Bureau of Public Roads renumbered the Hawaii Route System. The 1955 Hawaii Route Renumbering saw most of the conventions utilized by the current Hawaii State Route System established. Primary Hawaii Routes were given two digit numbers whereas Secondary Hawaii Routes were given three digit numbers. The Hawaii Routes were assigned in sequence for what Island/County they were located on coupled with what Federal Aid Program number they were tied to. In the case of O'ahu the Island was assigned numbers in the range of 60-99. In the case of Nimitz Highway it was assigned as Hawaii Route 92.
Hawaii Route 92 on Nimitz Highway can be seen constructed to Hawaii Route 61 at Nuuanu Boulevard on the 1959 Gousha Map of Hawaii. Ala Moana Boulevard is shown with no direct connection to Nimitz Highway.
According hawaiihighways.com what became Nimitz Highway had been planned as part of the cross-town Makai Arterial which would connect Honolulu to Hickam Army Airfield. The Makai Arterial was dropped during 1948 and the Mauka Arterial (future Intestate H-1) through Honolulu began to be developed instead.
On August 21st, 1959 Hawaii became the 50th State which saw it's profile rise significantly. The Interstate System in Hawaii was authorized as part of the 1960 Statehood Act. The 1960 Statehood Act authorized Interstates H-1, H-2 and H-3 on the Island of O'ahu.
On August 24th, 1968 the Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1968 was signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson. The Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1968 added an additional 1,500 miles to the Interstate Highway System which was to be funded through 1972. The Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1968 was the impetus for numerous Interstate proposals which would include the concept of Interstate H-4. Interstate H-4 was presented as a proposed highway by way of a October 1968 Hawaii of Transportation Document titled; Proposed Route H-4.
Proposed Route H-4 Section V describes the estimated cost of Interstate H-4. A fully double deck viaduct grade is stated to have an estimated cost of $300,684,000 dollars. A second cost estimate of $284,278,000 dollars is given for at-grade Interstate H-4 between the Ward Avenue Interchange and University Avenue Extension. The at-grade Interstate H-4 alternate is stated to be planned outside of the Ward Avenue Interchange-University Avenue Extension corridor as an elevated freeway.
From Interstate H-1 westbound Exit 25B (the Kapiolani Interchange) a ghost ramp to what would have been Interstate H-4 can be observed approaching Kapiolani Boulevard.


































Comments