Hawaii Route 64 is a 2.6 mile State Highway contained within the City of Honolulu. Hawaii Route 64 begins at Hawaii Route 92/Nimitz Highway and follows Sand Island Access Road and Sand Island Parkway to Sand Island State Recreation Area. Hawaii Route 64 is the only road to access Sand Island in the City of Honolulu which crosses the Honolulu Harbor Bridge.
Part 1; the history of Hawaii Route 64
Sand Island was originally known as Kamoku'akulikuli and came to be known as Quarantine Island following a quarantine station being constructed there during 1872. Quarantine Island was expanded during 1888 via use of landfill. Quarantine Island was used to impound ships attempting access Honolulu Harbor which had potentially contagious passengers. Quarantine Island can be seen on the 1899 Taylor Map of O'ahu just offshore from Honolulu.
The 1901 George Franklin Cram Map of Honolulu displays a low tide carriage road from Quarantine Island in addition to a Pier/Tramway to Quarantine Wharf. Quarantine Island was enlarged again via landfill during 1906 and was surrounded by a sea wall. During 1916 the Sand Island Military Reservation was established which led to numerous improvements to Sand Island and Honolulu Harbor.
Prior to the Statehood the first signed highways within Hawaii Territory came into existence during World War II. During World War II the territory of Hawaii saw an influx of military activity following the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7th, 1941. Numerous Military Routes and early Hawaii Routes were signed through the Hawaiian Territory to aid military personnel in navigating the islands. Military Highways were assigned US Route style shields whereas lesser highways were assigned an early variation of what is now the Hawaii Route Spade.
A 1946 Army Map of the Island of O'ahu shows no World War II era Hawaii Routes or roads accessing Sand Island. During World War II was used an Army Interment Camp which opened immediately after the attack on Pearl Harbor. The Sand Island Army Interment Camp housed Hawaiians of Japanese descent and others living in Hawaii born in Axis Power Countries. The Sand Island Army Interment Camp closed during March of 1943 with most of the prisoner population transferred to the Mainland United States or Honouliuli Interment Camp. A full version of the 1946 Army Map of O'ahu can be seen on hawaiihighways.com here.
Circa 1955 following the conclusion of World War II the United States Bureau of Public Roads renumbered the Hawaii Route System. The 1955 Hawaii Route Renumbering saw most of the conventions utilized by the current Hawaii State Route System established. Primary Hawaii Routes were given two digit numbers whereas Secondary Hawaii Routes were given three digit numbers. The Hawaii Routes were assigned in sequence for what Island/County they were located on coupled with what Federal Aid Program number they were tied to. In the case of O'ahu the Island was assigned numbers in the range of 60-99.
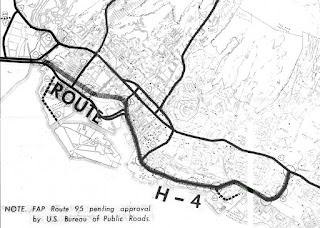
During 1959 Sand Island was turned over by the U.S. Army to the Territory of Hawaii. On August 21st, 1959 Hawaii became the 50th State which saw it's profile rise significantly. During April 1962 the Army Corps of Engineers completed the two-lane Lt. John R. Slattery Bridge as bascule draw span. The completion of the Lt. John R. Slattery Bridge saw Sand Island Access Road added to the Hawaii Route System as Hawaii Route 640. Hawaii Route 640 on Sand Island Access Road to the Lt. John R. Slattery Bridge can be seen on a 1968 concept drawing of Interstate H-4.



















Comments