Part 1; the history of US Route 30N in Pocatello
The City of Pocatello lies within Portneuf Valley and is named after Northern Shoshone Chief Pocatello. What became Pocatello began to see residential development during the 1880s and would formally become an established siding community of the Union Pacific Railroad in 1889. Bannock County was created in 1893 which saw Pocatello become the County Seat. The Academy of Idaho was established in Pocatello circa 1901 which now known as Idaho State University.
The future corridor of US Route 30N in downtown Pocatello can be see as part of the Old Oregon Trail and Evergreen National Highway on the 1925 Rand McNally Auto Trails Map of Idaho, Montana and Wyoming.
During November of 1926 the US Route System was approved by the AASHO. As noted in the Intro US Route 30N ("US 30N") westbound entered Pocatello via 5th Avenue with a multiplex of US 91. US 30N split from US 91 towards downtown Pocatello via Center Street onward towards Main Street. Main Street carried US 30N through downtown Pocatello westward towards American Falls. US 30N can be seen splitting from US 91 in the City of Pocatello on the 1927 Rand McNally Map of Idaho.
The route definition of US 30N in Idaho can be seen in an AASHO document dated to November 11th, 1926 (the day the US Route System was created). Pocatello is seen as part of the route definition for US 30N.
Early US 30N on Center Street in Pocatello utilized a viaduct structure which was constructed in 1911 (according to Idaho State University). The photo below can be seen on bridgehunter.com.
The Center Street Viaduct can be seen below in a photo sourced from Idaho State University.
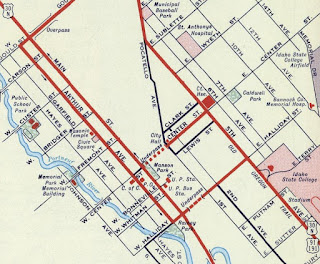
US 30N in Pocatello can be seen in clearer detail on the 1932 Idaho Bureau of Highways Map.
At some point US 30N in downtown Pocatello was split to a dual couplet alignment. Westbound US 30N followed the original alignment of the highway from 5th Avenue via Center Street and Main Street. Eastbound US 30N was shifted to a new alignment which followed Arthur Avenue through downtown and Halliday Street Subway via 1911 Union Pacific Railroad Underpass to 5th Avenue. The one-way couplets of US 30N in downtown Pocatello can be seen on the 1956 Shell Highway Map of Idaho.
The Halliday Street Subway can be seen in Idaho Historical Society photo below.
US 30N was approved by the AASHO Executive committee to be relocated out of downtown Pocatello during November of 1960. US 30N was shifted onto a multiplex of US 91/US 191 on 5th Avenue via northwest from Center Street to a new branching alignment at Oak Street. From Oak Street US 30N followed Garrett Way west via a total bypass of downtown Pocatello. The former alignment of US 30N in downtown Pocatello was approved to be signed as US 30N Business. The new alignment of US 30N is noted to have been signed as a truck bypass of downtown Pocatello for several years.
US 30S and US 30N in Idaho were approved to be consolidated into a singular mainline US 30 alignment by the AASHO Executive Committee during June of 1972. The consolidation of US 30 was spurred by the development of Interstate 80N and Interstate 15W. The singular US 30 in Idaho followed what had been US 30N including through Pocatello. Mainline US 30 subsequently assumed 1960 alignment of US 30N in the City of Pocatello. Since 1972 there has been minimal changes to US 30 within the City of Pocatello. It is unclear when the US 30N Business Route through downtown Pocatello was deleted.
Pictured below is the intersection of Center Street and Main Street in downtown Pocatello. Westbound US 30N would come in from the right side of the photo from the Center Street Underpass and turned right onto Main Street.
The Center Street Underpass is still a present structure carrying westbound only traffic on Center Street into downtown Pocatello.
A westward look on Center Street towards Main Street reveals what US 30N westbound would have looked like entering downtown Pocatello.
In 1965 the Benton Street Bridge was built as a replacement to the Halliday Street Underpass. The Benton Street Bridge for a time would have been part of the US 30N Business Route. The City of Pocatello recently finished rehabilitating the Benton Street Bridge which is featured below:
The Halliday Street Subway still exists but is now inaccessible as it has been buried under the Union Pacific Railroad. The Halliday Street Subway was excavated during the 1990s to make repairs to local storm drains which can be seen in the Idaho State University sourced photo below.






















Comments