North Carolina's passenger rail system had a record year in 2022. Quickly bouncing back from the drastic drop in ridership during the Covid-19 pandemic, the Raleigh-to-Charlotte service saw a record of over 522,000 riders in 2022. The four-times daily route (three on the Piedmont service and one on the Carolinian that continues to New York City) also had a record-breaking month of 55,493 travelers in October. The overall ridership numbers within the state do not include passengers that utilized stations on other intercity lines that run through the state. (Silver Star, Crescent, Palmetto, and Silver Meteor)
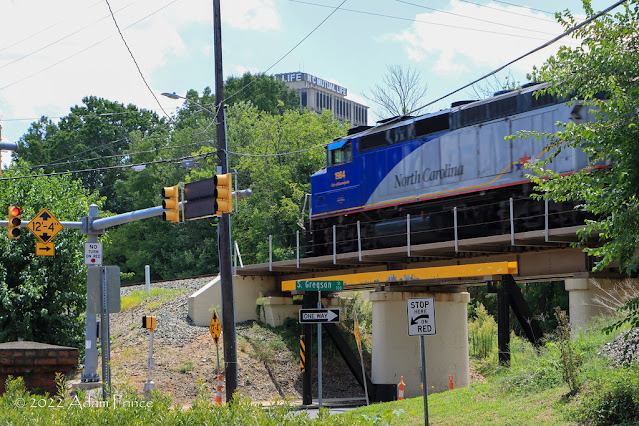 |
| A Southbound Piedmont Train approaches the Durham Train Station. More riders used the NCDOT-sponsored Piedmont service in 2022 than any other year prior. |
NC by Train celebrated the completion of the first phase of Charlotte's Gateway Station. The first test runs to the Uptown Charlotte station occurred in November. The new station will not be ready for passenger rail until at least 2025. The City of Charlotte is responsible for completing the station lobby, ticketing areas, and platform canopy. When completed, passengers will be able to disembark in Uptown Charlotte with transit connections to Charlotte's Gold Line street car.
While North Carolina can rightfully celebrate a growing ridership base - the eventual expansion of the intercity rail network within the state is still years away.
Charlotte Gateway Station and additional Piedmont Trips:
Gateway Station's full operation will be the key to the next expansion in North Carolina's rail service. When the new station opens, North Carolina will most likely add a fourth trip of the Piedmont, increasing service to five daily round trips between Raleigh and Charlotte.
Today, the Charlotte Amtrak Station is located at an outdated and undersized former Southern Railways Station on North Tryon Street, approximately 1.5 miles from Uptown. It lacks parking and good transit connections. The Lynx Blue Line is nearby but constitutes crossing over multiple railroad tracks, which obviously is not allowed.
The new station will most likely be an immediate success. Located in Uptown Charlotte, the new station will be within walking distance of Truist Park and Bank of America Stadium. With the NFL Panthers and MLS Charlotte FC both playing at Bank of America Stadium - the new station will allow for longer-distance fans (Greensboro and Raleigh) easy travel to the Queen City on game days. The connection to the Lynx Gold Line will provide direct access to the Spectrum Center (home of the NBA's Hornets) for concerts, basketball, and other events.
The current timetable for the Raleigh-Charlotte service is below. (As of March 2023)
| Train | Leave Raleigh | Arrive Charlotte | Train | Leave Charlotte | Arrive Raleigh |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piedmont 73 | 6:30 am | 9:40 am | Carolinian 80 | 6:45 am | 10:05 am |
| Piedmont 75 | 10:00 am | 1:10 pm | Piedmont 74 | 10:30 am | 1:41 pm |
| Piedmont 77 | 3:00 pm | 6:10 pm | Piedmont 76 | 3:15 pm | 6:26 pm |
| Carolinian 79 | 5:30 pm | 8:56 pm | Piedmont 78 | 7:00 pm | 10:11pm |
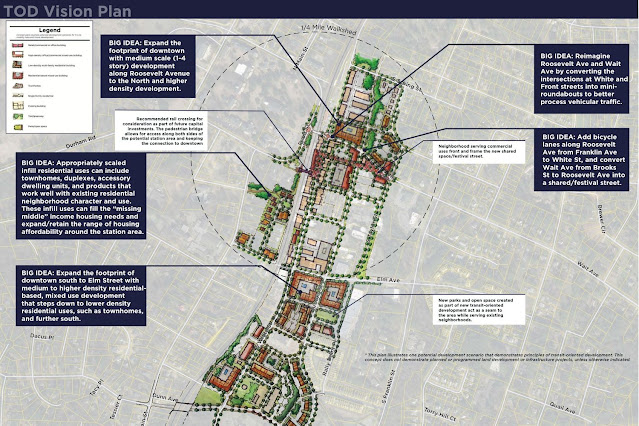 |
| Transit-Oriented Development Plan for Downtown Wake Forest - Town of Wake Forest |
While this study does not appear to discuss specific station locations - it is a good guess that new stops in Apex, Wake Forest, Sanford, Youngsville, Henderson, and Norlina are under consideration. Sanford and Wake Forest are already preparing for a return of passenger rail service to their communities.
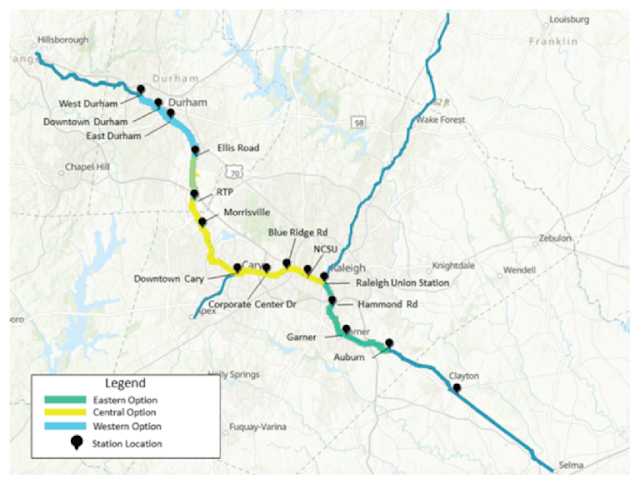 |
| The station plan for the Triangle Commuter Rail proposal. Future extensions are the thinner lines. (GoTriangle) |
GoTriangle has completed a feasibility study for commuter rail. The study split the Durham to Garner route into three sections (Western, Central, and Eastern). Although there is no timeline on when construction would begin, the study estimated anywhere from 8-12 years to complete depending on the section. Further expansion east into Johnston County towards Clayton would require additional funding. Additionally, continuing the train north and west beyond Ellis Road into Downtown Durham currently exceeds any of Durham County's transit budget.

Comments