Interstate 40 Spur is 0.794-mile hidden State Highway which exists in the city of Barstow, California. Interstate 40 Spur originates at National Trails Highway and follows Main Street west to the vicinity of Coolwater Lane. Interstate 40 Spur is a former segment of US Route 66 which was bypassed during July 1961. The purpose of Interstate 40 Spur is to permit movement from westbound Interstate 40 to northbound Interstate 15.
The history of Interstate 40 Spur
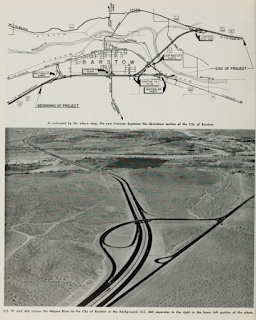
The September/October 1961 California Highways & Public Works announced the opening of the Barstow Bypass. The Barstow Bypass was primarily a component of Interstate 15 which opened on July 5, 1961. The Barstow Bypass included the exit ramp to Interstate 40 and the first stub of the freeway eastward towards Needles. The mainlines of US Route 66 and US Route 91 were relocated onto the new freeway bypass whereas the previous surface routings were retained as a Business Routes. Main Street (former US Route 66) between Interstate 40 and Interstate 15 was retained as a spur of Legislative Route Number 58 (LRN 58). This section of State Highway was necessary to retain to due to the Interstate 15/Interstate 40 interchange not permitting traffic to transition from westbound Interstate 40-to-northbound Interstate 15 and southbound Interstate 15-to-eastbound Interstate 40.
US Route 66 was approved to be truncated from Santa Monica to US Route 95 in Needles by the AASHO on November 14, 1963. Signage of US Route 66 would not be truncated from Pasadena to US Route 95 until Interstate 40 was completed through the Bristol Mountains in 1972. The US Route 66 Business Route on Main Street in Barstow would be swapped without application to Interstate 15 Business.
As part of the wider 1964 State Highway Renumbering the Legislative Route Numbers were dropped. The spur facility of LRN 58 on Main Street between Interstate 40-Interstate 15 was re-designated as Interstate 40 Spur. Interstate 40 Spur remains minimally signed as Interstate 15 Business. Interstate 40 Spur can be seen below as presently configured in the Caltrans Postmile Tool.
Note, Caltrans recognizes all categories of their highway inventory as "State Routes." To that end Interstate 40S is not considered part of the Interstate System by the Federal Highway Administration and does not appear in their mileage calculations for Interstate 40.












Comments