This blog is Part 2 of a three part series on of the Shoreline Highway segment of California State Route 1 and features a drive through Sonoma County. Part 1 found below discusses the development of the Shoreline Highway and features a drive through Marin County.
Chapter 3; California State Route 1/Shoreline Highway through Sonoma County
Upon entering Sonoma County CA 1 northbound makes a left turn at Valley Ford Road at Postmile SON 0.18.
CA 1 northbound jogs westerly and enters Valley Ford at Postmile SON 2.07.
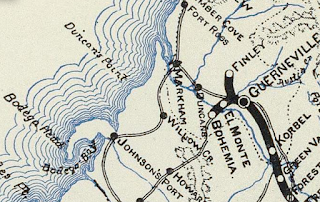
The entomology of "Valley Ford" refers to a time when a nearby Native American and Spanish trail required "fording" Americano Creek. The first American inhabitants of Valley Ford arrived in 1849 when the Fowler Brothers purchased a tract of land. Subsequently the small community of Valley Ford to began to develop. Valley Ford came to prominence in 1876 when the NPCRR extended through it's line through the community and built a depot. Valley Ford and the Fowler property can be seen on the 1866 Bowers Map of Sonoma County.
The NPCRR and Valley Ford can be seen on the 1890 George Franklin Cram Railroad Map of California.
What would become CA 1 in Valley Ford during the 19th Century as seen on wendroot.com.
The structure on the right is the 1893 Dairyman's Bank Building whereas the Valley Ford Hotel on the left was constructed in 1864.
CA 1 northbound passes Valley Ford Estero Road in Valley Ford which is signed as access to Dillon Beach.
At Postmile SON 2.73 CA 1 northbound intersects it's original alignment at Freestone Valley-Valley Ford Road. Modern CA 1 turns left onto the Valley Ford Cutoff.
CA 1 northbound jogs west and intersects it's original alignment at Bodega Highway located at Postmile SON 5.37.
CA 1 northbound continues westward and follows Bay Highway into Bodega Bay at Postmile SON 10.40.
Upon entering Bodega Bay CA 1 northbound traffic is given a 30 foot length advisory for the next 154 miles. The sign is while oddly placed it is not inaccurate.
Bodega Bay was the site of the first Russian community in California which was known as Port Rumyantsev. Port Rumyantsev was constructed in 1809 and would ultimately play a part in the development of Fort Ross. The actual Bodega Bay is named after Spanish Naval Officer Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra, The Russian settlers were later bought out by John Sutter during the Mexican period of Alta California in 1841. In 1843 Captain Stephen Smith returned to Bodega Bay after visiting it in 1841 and occupied structures abandoned by the Russians. Smith moved to a new adobe in 1851 which was constructed by the Fowler Brothers of Valley Ford. Smith would become a well known rancher in the area and his estate was dispersed following his death in 1855. Bodega Bay and Bodega Port can be seen on the 1866 Bowers Map of Sonoma County.
Bodega Bay and nearby Bodega are largely famous for being the backdrop of the 1963 Alfred Hitchcock movie "The Birds." More regarding the filming of "The Birds" can be found on the bodegabay.com stub page. (Note; the schoolhouse scene below was filmed in Bodega)
CA 1 northbound turns north passing through Bodega Bay. Upon departing Bodega Bay CA 1 northbound crosses Salmon Creek at Postmile SON 12.49.
CA 1 north of Bodega Bay passes by numerous beach pullouts which culminates with Goat Rock Beach Road at Postmile SON 19.16. Much of present CA 1 from Duncans Point north to the Russian River was established on or near the former right-of-way of Duncans Railroad (see the Jenner section below for more details).
CA 1 northbound passes through Bridgehaven and crosses the Russian River at Postmile SON 19.82. Upon crossing the Russian River CA 1 northbound intersects CA 116. From the CA 116 intersection Fort Bragg is signed as 99 miles away on CA 1.
CA 1 northbound enters Jenner at Postmile SON 21.20.
Jenner (or "Jenner-by-the-Sea") lies at the mouth of the Russian River and was settled in 1854 by Dentist Elijah Jenner. In time a small community would develop around the Jenner homestead which came to be known as Jenner Gulch. The Jenner household can be seen on the 1866 Bowers Map of Sonoma County at High Rock on the north bank of the Russian River opposite Duncanville and the Duncans Railroad.
A full view of Duncans Railroad on the 1866 Bowers Map of Sonoma County reveals it's terminus at Duncans Landing. Duncanville received Post Office Service in 1862 but was frequently flooded due to it being located at the mouth of the Russian River. Duncanville was destroyed in 1876 by flooding on the Russian River and the town site was moved five miles up river to the east to what is now known as Duncans Mills.
The relocated Duncans Mills can be seen upstream on the Russian River along what is now CA 116 on the 1898 San Francisco & North Pacific Railway Company Map.
CA 1 northbound passes through Jenner. Upon departing Jenner CA 1 northbound is signed as 11 miles from Fort Ross.
CA 1 begins to climb onto the steep coastal bluffs north of Jenner. At Postmile SON 26.39 CA 1 northbound intersects Meyers Grade Road.
CA 1 north of Meyers Grade Road continues to follow the coastal bluffs before leveling out approaching Fort Ross State Historic Park. At Postmile SON R33.03 CA 1 northbound intersects Fort Ross Road which acts as access to Fort Ross State Historic Park.
Fort Ross State Historic Park is one of the oldest in the California State Park System having been established in 1906. As noted above Port Rumyantsev located in Bodega Bay was settled as a Russian Colony in 1809. In 1812 Ivan Kuskov of the Russian-American Company set out from Alaska to the site of the Kashaya-Pomo Village of Metini to establish a colony. Kuskov's expedition included 80 Alaskan Natives and 25 Russians which would soon construct homes in addition to a stockade. Kuskov's colony was organized to establish a footing for hunters, an outpost for trade with the Spanish and wheat harvesting. On August 30th, 1812 Fort Ross was formally dedicated ("Ross" being a reference to "Imperial Russia"). Through the 1820s Fort Ross was expanded upon as it became a more established settlement. As noted above the Russian-American Company was bought out by John Sutter in 1841. Fort Ross changed hands numerous times during the 19th Century before being purchased by the California Historical Landmarks Committee in 1903.
The Alexander Rotchev house pictured below (from the State Parks brochure) is the last remaining original structure at Fort Ross. The Alexander Rotchev house was renovated in 1836 which likely ensured it's survival. Additional structures such as; the first Russian Orthodox Church south of Alaska, the stockade, fur house, manager's house and several others have been reconstructed by the California State Parks Service.
Fort Ross can be seen on the 1833 Holmes Map of Fredonia or The United States of North America.

























































































































































































































Comments