Dinosaur Point Road east of Pacheco Pass to the waters of the San Luis Reservoir is the original alignment of California State Route 152. Since July 1965, California State Route 152 has been realigned east of Pacheco Pass via a modernized expressway. The original alignment of California State Route 152 on occasion reemerges from the San Luis Reservoir at Dinosaur Point. Pictured above as the blog cover is the original alignment of California State Route 152 at Dinosaur Point disappearing eastward into the waters of the San Luis Reservoir. Below California State Route 152 can be seen passing through what is now the San Luis Reservoir east of Pacheco Pass on the 1935 Division of Highways Map of Merced County.
The present site of the San Luis Reservoir during the era of Alta California was part of Rancho San Luis Gonzaga. Rancho San Luis Gonzaga was granted to Francisco Jose Rivera of Monterey during 1841. Rivera ultimately never occupied Rancho San Luis Gonzaga. During 1843 large portions of Rancho San Luis Gonzaga were granted to Juan Carlos Pacheco and Captain Jose Maria Meija. Within days of being granted part of Rancho San Luis Gonzaga, Captain Meija would gift his share to Pacheco. Rancho San Luis Gonzaga even by the 1840s was already a well-established crossing the Diablo Range and would come to be known as Pacheco Pass.
An established trail over Pacheco Pass had been use by the local Yokut Tribes long before the arrival of Europeans to California. The first documented European crossing of Pacheco Pass was made in 1805 by a party led by Spanish Army Officer Gabriel Moraga.
During the American period Andrew Firebaugh constructed a tolled stage road across Pacheco Pass to Bell Station. Firebaugh's toll road was completed by 1857 and was part of the Butterfield Overland Mail route between 1858-1861. A primitive path over Pacheco Pass to Gilroy can be seen on the 1857 Britton & Rey's Map of California.
The Butterfield Overland route over Pacheco Pass is touched on in the September 1950 California Highways & Public Works.
The more established Pacheco Pass Toll Road can be seen on the 1873 Bancroft's Map of California. In 1879 Santa Clara County and Merced County purchased the Pacheco Pass Toll Road, rebuilt it on a new grade and made it a public highway.
The history of State Highways over Pacheco Pass begins in 1915 with the passage of the Second State Highway Bond Act. Legislative Route Number 32 ("LRN 32") was added to the State Highway System with the following definition:
"an extension connecting the San Joaquin valley trunk line (LRN 4/Inland Route) at a point between the city of Merced in Merced County and the city of Madera in Madera County with the coast trunk line (LRN 2/Pacific Highway) at or near the city of Gilroy in Santa Clara County, through Pacheco Pass, by the most direct and practical route."
The entirety of LRN 32 between Califa and Gilroy by way of Pacheco Pass appears on the 1917 California State Automobile Map.
According to the March/April 1951 California Highways & Public Works the State completed construction of a new alignment for LRN 32 over Pacheco Pass by 1923. The 1923 alignment of LRN 32 was a replacement for the 1879 Santa Clara County/Merced County highway.
During 1933 LRN 32 would be extended west from Gilroy via Hecker Pass to Watsonville. The entirety of LRN 32 was announced as California State Route 152 in the August 1934 California Highways & Public Works.
Below California State Route 152/LRN 32 can be seen passing through what is now the San Luis Reservoir east of Pacheco Pass on the 1935 Division of Highways Map of Merced County.
Plans for the construction of San Luis Dam were completed by 1961 and construction broke ground during August 1962. The construction of San Luis Dam necessitated the relocation of California State Route 152/LRN 32 due to it being located int what was to become the San Luis Reservoir. The relocation of California State Route 152 would see it realigned north of the planned San Luis Reservoir east from Pacheco Pass.
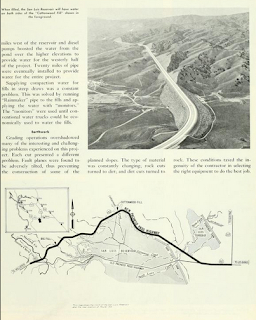
The realignment of California State Route 152 north of the planned San Luis Reservoir is discussed in the July/August 1965 California Highways & Public Works. The realignment of California State Route 152 is cited to be 12 miles in length originating from the Merced/Santa Clara County Line and extending eastward as a divided road to California State Route 207. The new expressway alignment of California State Route 152 east of Pacheco Pass was opened via dedication ceremony on April 29th, 1965. The San Luis Reservoir would not be completed until 1967 which would see the original alignment of California State Route 152 east from Dinosaur Point inundated. The original alignment of California State Route 152 at Dinosaur Point became a boat launch for the San Luis Reservoir Recreation Area.
Part 2; exploring the original alignment of California State Route 152 east from Pacheco Pass to Dinosaur Point
As modern California State Route 152 eastbound approaches Pacheco Pass in Santa Clara County the original soft transition can be seen razed to the right approaching Dinosaur Point Road. Pacheco pass lies at an elevation of 1,368 feet above sea level.






















































Comments