Blue Ridge Road (Tulare County Mountain Road 276) is a rural highway located in the Sierra Nevada range northeast of Springville. The corridor is approximately 8.5 miles and accesses the namesake Blue Ridge located at 5,731 feet above sea level. Modern Blue Ridge Road was constructed during the early 1950s and carries a sustained grade of approximately 6%. The current roadway was built as a replacement for Grouse Valley Road and served as access to the Blue Ridge overlook tower. Said tower was in operation between 1930-2010 as a joint venture between California Department of Forest & Fire and the United States Forest Service.
Part 1; the history of Blue Ridge Road
The 5,731 foot high Blue Ridge located above Grouse Valley offers an outstanding view east into the Sierra Nevada range mostly comprising Sequoia National Forest. The site was selected for a lookout tower which was to be used jointly by the California Department of Forest & Fire and the United States Forest Service. An $1,800 allocation for the development of the Blue Ridge lookout tower was announced in the October 27, 1930, Los Angeles Times.
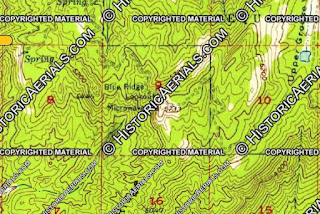
The 1935 Division of Highways Map of Tulare County shows the Blue Ridge lookout tower as part of the Grouse Valley Airport complex located in Township 19S, Range 29E. The tower is shown connected to Yokohl Valley Drive at Township 19S, Range 28E along a road descending Blue Ridge westward through Grouse Valley and following the course of Van Gordon Creek.
The lookout tower at Blue Ridge was joined by a microwave broadcasting facility by the early 1950s. The facility is described as having reopened for California Department of Forest & Fire Service in the May 18, 1952, Fresno Bee. Modern Blue Ridge Road seems to have been part of the improvements to the Blue Ridge lookout tower facility as it appears on era 1955 aerial imagery and the 1958 United States Geological Survey map (both courtesy historicaerials.com).
In modern times Blue Ridge Road was assigned as Tulare County Mountain Road 276. The Blue Ridge lookout tower was removed in 2010 and shipped to the Tulare County Fairgrounds as a display piece. Blue Ridge currently houses transmitter facilities for KDUV-FM Visalia.
Part 2; a drive on Blue Ridge Road
Westbound Blue Ridge Road begins at Tulare County Route J37 (Balch Park Road) at approximately 3,000 feet above sea level.
As Blue Ridge Road begins it faces Dennison Peak which is located at 7,218 feet above sea level. Traffic is advised there is no outlet ahead.
Blue Ridge Road jogs initially northward and crosses the North Fork Tule River.
Beyond the North Fork Tule River traffic can view Blue Ridge and the radio facility atop it from the roadway. Blue Ridge Road has an approximately 6% sustained incline grade from Balch Park Road west to Blue Ridge.
Blue Ridge Road narrows to one-lane width upon entering Sequoia National Forest. The roadway intersects Tulare County Mountain Road 270 shortly upon entering the National Forest boundary.
Blue Ridge Road continues northwest and crosses the Kramer Creek Bridge (near Postmile 4.00) at approximately 4,100 feet above sea level.
Blue Ridge Road turns westward and begins the steepest part of the ascent to the Blue Ridge radio facility. Near Postmile 6.00 the roadway interests the gate to the Upper Grouse Valley cabins which can be rented from the Forest Service. Upper Grouse Valley is located at approximately 4,800 feet above sea level.
Blue Ridge Road continues west and terminates at approximately Postmile 8.50 at the Blue Ridge radio facility.
The roadway continues to the top of Blue Ridge. A roadway continuing west of the tower appears on some maps as Grouse Valley Road, but it no longer connects to Yokohl Valley Drive.
The view east along Blue Ridge Road into the Sierra Nevada from the radio facility can be seen below. Dennison Peak and nearby Dennison Mountain are easily identified.
Blue Ridge is now part of the 897-acre Blue Ridge National Wildlife Refuge. Said refuge was established in 1982 and was set aside as a roosting ground for the California Condor. The refuge is managed by the United States Fish & Wildlife Service.
The descent east on Blue Ridge Road offers numerous vistas of Dennison Peak and the canyons draining into the North Fork Tule River.


















































































Comments