Arizona State Route 71 is a 24.16-mile state highway located in the Wickenburg area. Arizona State Route 71 begins at US Route 60 in Aguila of Maricopa County and terminates to the northeast at Arizona State Route 89 at Congress Junction of Yavapai County. The current iteration of Arizona State Route 71 was created during 1936 as part of a proposed extension of US Route 93. The original Arizona State Route 71 corridor initially spanned between Solomonville to Clifton. The original Arizona State Route 71 was extended over the Coronado Trail to Springerville during 1928 and was eventually absorbed by an extended Arizona State Route 81 during 1937. The current Arizona State Route 71 can be seen on the 1951 Gousha Highway Map of Arizona.
The history of Arizona State Route 71
The original Arizona State Route 71 was created by the Arizona Highway Commission along with the initial set of State Highways on September 9, 1927. The original Arizona State Route 71 was aligned from Clifton south to US Route 180 near Solomonville. The original Arizona State Route 71 can be seen on the 1927 Arizona Highway Commission Map.
The description of the original Arizona State Route 71 appears in the January 1928 Arizona Highways.
The June 1928 Arizona Highways announced the Coronado Trail north of Clifton and Morenci had been added to the State Highway System.
The August 1928 Arizona Highways was the first volume to reference Arizona State Route 71 extended north of Clifton via the Coronado Trail to Springerville. The Coronado Trail north of Morenci is noted to have opened as a modernized highway on June 19, 1926. The Coronado Trail followed the path explored by Francisco Vasquez de Coronado during his search for the Seven Cities of Gold.
The original Arizona State Route 71 can be seen extended north of Clifton along the Coronado Trail to US Route 70 near Springerville on the 1931 Clason's Map of Arizona.
In 1937 the original Arizona State Route 71 was deleted when Arizona State Route 81 was extended north to Sanders via the Coronado Trail. The Coronado Trail would become part of US Route 666 during December 1938 and US Route 191 during June 1992. The corridor of the original Arizona Stare Roure 71 is shown to be replaced with Arizona State Route 81 on the 1937 Gousha Map of Arizona.
What was to become modern Arizona State Route 71 was adopted by 1936 right-of-way resolution P-574.
During September 1935 US Route 93 had been extended into Arizona to a terminus concurrent with US Route 466 to Kingman. The State Legislature had adopted proposed extension of US Route 93 on March 13, 1937. The proposed extension of US Route 93 was planned to be aligned to Aguila via Wikieup, Signal and Alamo.
On May 26, 1937, the Arizona State Highway engineer submitted a proposal to extend US Route 93 from Kingman to Nogales. The proposal included a temporary routing for US Route 93 which would be concurrent with US Route 89 from Ashfork south to Wickenburg via Prescott. The permanent routing of US Route 93 was similar as what had been adopted by the State Legislature during the previous March. Instead of being aligned to Aguila, the planned extension US Route 93 was planned to be aligned through Wickenburg.
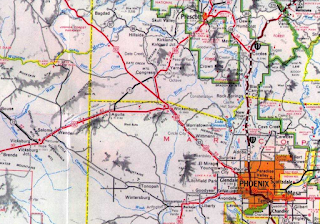
The 1951 Gousha Highway Map of Arizona depicts numerous highways passing through Wickenburg. US Route 89 and Arizona State Route 93 are shown entering Wickenburg via Tegner Street from Congress Junction. US Route 60 and US Route 70 are shown passing through Wickenburg via Wickenburg Way. East of Tegner Street US Route 60, US Route 70 and US Route 89 are shown multiplexing towards Phoenix. Arizona State Route 71 is displayed as having inherited the initial planned routing of US Route 93 to Aguila. Arizona State Route 93 between Kingman and Wickenburg formally adopted during March 1946 following completion of the highway.
On January 15, 1958, the Arizona Highway Department submitted an application to AASHO to extend US Route 93 to Wickenburg. The AASHO Executive Committee rejected the application on June 26, 1958, due to the permanent alignment Arizona State Route 93 not having been constructed south of Arizona State Route 71.
The new routing of Arizona State Route 93 south of Arizona State Route 71 was formally adopted on November 6, 1961.
The Arizona Highway Department submitted a request to extend US Route 93 to Nogales on April 28, 1965. The AASHO Executive Committee only granted an extension of US Route 93 to US Route 89 north of Wickenburg. The rejection of US Route 93 being extended to Nogales was due to the routing being completely concurrent with US Route 89 south of Wickenburg. The completion of US Route 93 to Wickenburg saw Arizona State Route 71 extended to US Route 89 at Congress Junction.
The 1971 Arizona Highway Department map depicts the extension of Arizona State Route 71 to US Route 89 at Congress Junction.



























Comments