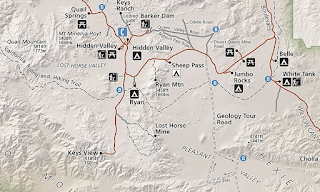
On a recent visit to Joshua Tree National Park I was looking for a long hike that involved something significant from the mining period in the San Bernarindo Mountains. I found what I was looking for on the Lost Horse Mine Trail and Lost Horse Loop Trail.
The Lost Horse Mine was one of the over 300 mining claims which were staked in what is now Joshua Tree National Park. The Lost Horse Mine is located on a peak of the San Bernardino Mountains of the Mojave Desert between Lost Horse Valley to the west and Pleasant Valley to the east. The Lost Horse Mine is located in Riverside County about 15 miles north of the City of Indio.
The Lost Horse Mine was one of the few successful mining claims in the San Bernardino Mountains and was in operation from 1894 to 1931. The Lost Horse Mine produced approximately 10,000 ounces of gold and 16,000 ounces of silver which amounts to about $5,000,000 in modern dollars. The Lost Horse Mine was founded off of a claim which was located in 1890. The Lost Horse Mine claim was purchased by Johnny Lang and three partners for $1,000 dollars. The initial mill at the Lost Horse Mine was initially only a two-stamp. The "Lost Horse" name comes from a story in 1890 where Johnny Lang encountered rustlers who threatened him after stealing his horses.
In 1895 Johnny Lang's investment partners were bought out by J.D. Ryan. Ryan arranged for a ten-stamp mill to be moved from a Colorado River claim to the Lost Horse Mine. The ten-stamp mill was powered by a steam engine which was located 3.5 miles away at Ryan's Ranch. The steam engine was powered by trees from the peaks near the Lost Horse Mine which never regrew.
The Lost Horse Mine ran 24 hours a day and was in operation until 1905 when a fault line was hit which shifted the vein carrying ore out of reach. During operating years of the Lost Horse Mine Lang was discovered to being stealing mineral ore for himself out of the stamp mill. Lang was threatened with being charged criminally by Ryan unless he sold his shares to the Lost Horse Mine. The Lost Horse Mine after 1905 operated sporadically via lease agreements. Lang apparently had returned to the Lost Horse Mine in the 1920s to find some of the mineral ore he had hidden but it isn't known if he succeeded. The Lost Horse Mine was last worked in 1931 when 600 tons of mine tailings were processed with cyanide due to a spike in gold prices. In August of 1936 Joshua Tree National Monument was established which annexed the Lost Horse Mine.
All of the above information was sourced from the National Park Service. The National Park Service article on the Lost Horse Mine can be found below:
NPS.gov on the Lost Horse Mine
My approach to the Lost Horse Mine Trail was from Keys View Road in Lost Horse Valley where I turned east onto the Lost Horse Mine Road. Lost Horse Valley lies at an elevation of 4,384 feet above sea level.
Lost Horse Mine Road is a single-lane dirt surface. There are a couple soft points and rocks on the road but it isn't anything that a normal car can't handle. The Lost Horse Mine Road ends about 0.6 miles east of Keys View Road at the trailheads for the Lost Horse Mine Trail and Lost Horse Loop Trail.
The Lost Horse Loop Trailhead is located at the entrance of the parking lot. The Lost Horse Loop Trail is signed as 6.2 miles overall and 4.2 miles from the Lost Horse Mine.
The Lost Horse Mine Trailhead is a lot of more obvious since it essentially was the Lost Horse Mine Road. The Lost Horse Mine is signed as 2 miles to the east of the parking lot. Since I was interested in getting to the Lost Horse Mine before the weekend crowd I headed out on the Lost Horse Mine Trail first.
The Lost Horse Mine Trail begins with a short historical information station.
The trail to the Lost Horse Mine is pretty easy and bears some evidence of grading still. The National Park Service lists the Lost Horse Mine Trail as moderate in difficulty and gaining 550 feet in elevation.
On the wash at the bottom of the hill below I found the first of many mining structures in a wash. In the distance Pleasant Valley can be seen.
The structure in the wash appears to be a miner's hut. The structure was stone and appears to have been very minimalist.
Ascending over the next hill offers the first glimpse at the Lost Horse Mine.
Tailings are strewn on the mountain side in places along the Lost Horse Mine Trail.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail begins at the terminus of the Lost Horse Mine Trail beneath the stamp mill.
I climbed up the remainder of the Lost Horse Mine Road to the mining complex itself. The Park Service has recently stabilized several collapsing mine shafts which threatened to take the remaining parts of the ten stamp mill. On the way up to the stamp mill part of the 3.5 mile steam line is easily observed. The ten stamp mill lies beyond a fence line but appears to have weathered more than a century fairly well. The Lost Horse Mine lies at an elevation of 5,003 feet above sea level.
Ascending onto the Lost Horse Loop Trail southward offers a overview of the Lost Horse Mine Complex.
There is a wide vista of Pleasant Valley on the Lost Horse Loop Trail immediately south of the Lost Horse Mine. Apparently this peak is known as Lost Horse Mountain and lies at 5,313 feet above sea level.
The Park Service rates the Lost Horse Loop Trail as difficult which is probably because of the mile south of the Lost Horse Mine which is largely rocky and steep.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail begins to swing westward and starts to level out. The remains of the Optimist Mine are encountered which essentially is just a chimney and rusted bed frame. The Optimist Mine apparently was a complete failure and never produced much if any gold.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail begins to descend into a Joshua Tree Forest with brief glimpses of the 10,834 foot San Jacinto Peak in the distance.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail swings north through a series of washes in a Joshua Tree Forest which is the easiest segment.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail terminates back at the Lost Horse Mine Road parking lot.
The Lost Horse Mine was one of the few successful mining claims in the San Bernardino Mountains and was in operation from 1894 to 1931. The Lost Horse Mine produced approximately 10,000 ounces of gold and 16,000 ounces of silver which amounts to about $5,000,000 in modern dollars. The Lost Horse Mine was founded off of a claim which was located in 1890. The Lost Horse Mine claim was purchased by Johnny Lang and three partners for $1,000 dollars. The initial mill at the Lost Horse Mine was initially only a two-stamp. The "Lost Horse" name comes from a story in 1890 where Johnny Lang encountered rustlers who threatened him after stealing his horses.
In 1895 Johnny Lang's investment partners were bought out by J.D. Ryan. Ryan arranged for a ten-stamp mill to be moved from a Colorado River claim to the Lost Horse Mine. The ten-stamp mill was powered by a steam engine which was located 3.5 miles away at Ryan's Ranch. The steam engine was powered by trees from the peaks near the Lost Horse Mine which never regrew.
The Lost Horse Mine ran 24 hours a day and was in operation until 1905 when a fault line was hit which shifted the vein carrying ore out of reach. During operating years of the Lost Horse Mine Lang was discovered to being stealing mineral ore for himself out of the stamp mill. Lang was threatened with being charged criminally by Ryan unless he sold his shares to the Lost Horse Mine. The Lost Horse Mine after 1905 operated sporadically via lease agreements. Lang apparently had returned to the Lost Horse Mine in the 1920s to find some of the mineral ore he had hidden but it isn't known if he succeeded. The Lost Horse Mine was last worked in 1931 when 600 tons of mine tailings were processed with cyanide due to a spike in gold prices. In August of 1936 Joshua Tree National Monument was established which annexed the Lost Horse Mine.
All of the above information was sourced from the National Park Service. The National Park Service article on the Lost Horse Mine can be found below:
NPS.gov on the Lost Horse Mine
My approach to the Lost Horse Mine Trail was from Keys View Road in Lost Horse Valley where I turned east onto the Lost Horse Mine Road. Lost Horse Valley lies at an elevation of 4,384 feet above sea level.
Lost Horse Mine Road is a single-lane dirt surface. There are a couple soft points and rocks on the road but it isn't anything that a normal car can't handle. The Lost Horse Mine Road ends about 0.6 miles east of Keys View Road at the trailheads for the Lost Horse Mine Trail and Lost Horse Loop Trail.
The Lost Horse Loop Trailhead is located at the entrance of the parking lot. The Lost Horse Loop Trail is signed as 6.2 miles overall and 4.2 miles from the Lost Horse Mine.
The Lost Horse Mine Trailhead is a lot of more obvious since it essentially was the Lost Horse Mine Road. The Lost Horse Mine is signed as 2 miles to the east of the parking lot. Since I was interested in getting to the Lost Horse Mine before the weekend crowd I headed out on the Lost Horse Mine Trail first.
The Lost Horse Mine Trail begins with a short historical information station.
The trail to the Lost Horse Mine is pretty easy and bears some evidence of grading still. The National Park Service lists the Lost Horse Mine Trail as moderate in difficulty and gaining 550 feet in elevation.
On the wash at the bottom of the hill below I found the first of many mining structures in a wash. In the distance Pleasant Valley can be seen.
The structure in the wash appears to be a miner's hut. The structure was stone and appears to have been very minimalist.
Ascending over the next hill offers the first glimpse at the Lost Horse Mine.
Tailings are strewn on the mountain side in places along the Lost Horse Mine Trail.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail begins at the terminus of the Lost Horse Mine Trail beneath the stamp mill.
I climbed up the remainder of the Lost Horse Mine Road to the mining complex itself. The Park Service has recently stabilized several collapsing mine shafts which threatened to take the remaining parts of the ten stamp mill. On the way up to the stamp mill part of the 3.5 mile steam line is easily observed. The ten stamp mill lies beyond a fence line but appears to have weathered more than a century fairly well. The Lost Horse Mine lies at an elevation of 5,003 feet above sea level.
Ascending onto the Lost Horse Loop Trail southward offers a overview of the Lost Horse Mine Complex.
There is a wide vista of Pleasant Valley on the Lost Horse Loop Trail immediately south of the Lost Horse Mine. Apparently this peak is known as Lost Horse Mountain and lies at 5,313 feet above sea level.
The Park Service rates the Lost Horse Loop Trail as difficult which is probably because of the mile south of the Lost Horse Mine which is largely rocky and steep.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail begins to swing westward and starts to level out. The remains of the Optimist Mine are encountered which essentially is just a chimney and rusted bed frame. The Optimist Mine apparently was a complete failure and never produced much if any gold.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail begins to descend into a Joshua Tree Forest with brief glimpses of the 10,834 foot San Jacinto Peak in the distance.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail swings north through a series of washes in a Joshua Tree Forest which is the easiest segment.
The Lost Horse Loop Trail terminates back at the Lost Horse Mine Road parking lot.





























































Comments